Derivatives And Its Basics
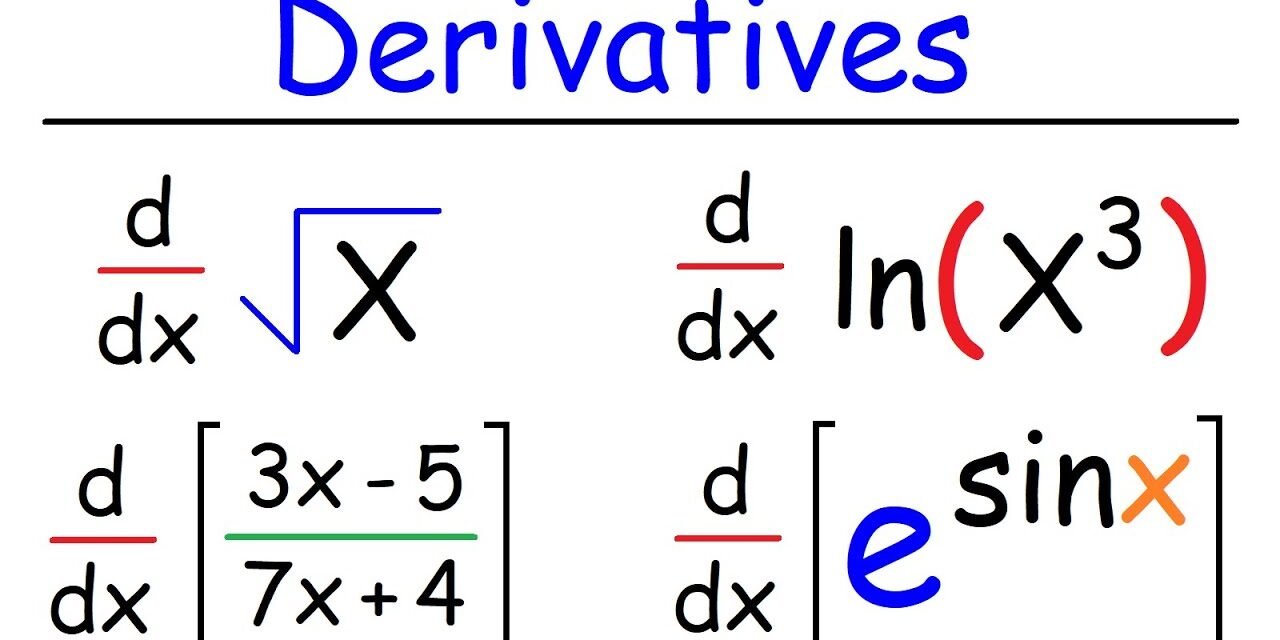
Derivatives are instruments that have several uses, including risk management and speculation. Risk management is an integral part of financial management and operations, and the use of derivatives helps a company reduce risk. On the other hand, belief involves a high degree of risk, but it can lead to profit.
The basics of derivatives
To understand how to compute derivatives, you should be familiar with the definition of a function. You can determine its product by adding its limit or considering its difference quotient. Using the same rules, you can also choose the derivative of a more complicated function. You will find these rules here. If you would like to learn more about our products, visit our website.
A good understanding of derivatives is a prerequisite for understanding the investment banking industry, and it also gives you a foundation for analyzing more complex financial transactions. This course will introduce you to the basics of derivatives and how they are related to one another. You can use the system to understand different derivatives and how they can be used to manage risk.
A derivative is the rate of change of a quantity related to a point. For example, the derivative of f(x) is f prime x. However, instead of writing Dx, you should write dx. In addition, instead of using Dx, you should use d as D stands for Delta. You can also write derivatives of a function like f/x as df/dx.
How to use derivatives
Derivatives allow investors to enter and exit a market at any given time. Derivatives are useful in many different areas, including investment, hedging, and trading. Although many believe that derivatives are used solely for trading or investment, they have many other uses. Big fund managers and ace investors, such as Warren Buffet, use derivatives to improve their entry prices into the market.
Derivatives are a powerful tool for measuring change, and they are used in the government’s population censuses, in various types of sciences, and in many other fields. Regardless of your profession, knowing how to use derivatives is a valuable skill to have. Learning as much as possible about this topic early in life is important, as this will help you apply it effectively.
The derivative is a measure of the slope of a function at any given point, often notated as dy/dx. It gives you local extrema, or 0’s, on a graph and can help you find useful characteristics about the function.
The risks and benefits of derivatives
Derivatives are an important tool in financial management. They allow investors to leverage their investments and profit from price fluctuations of underlying assets. For example, a derivative could yield a return of 10% when the underlying asset only yields 1%. However, these investments are often unregulated, which can lead to problems.
One of the benefits of derivatives is their ability to increase financial market efficiency. Since the underlying asset and its derivative are often in equilibrium, they can provide organizations with access to markets and assets they otherwise wouldn’t have access to. For example, a pension fund managing a large portfolio of corporate bonds can use derivative contracts to protect their value. Similarly, interest rate swaps are an effective way for investors to obtain a lower interest rate than they could get from direct borrowing.
Another benefit of derivatives is that they enable businesses to transfer risks to other parties. Using derivatives, firms can reduce the risk of bad harvests, adverse market fluctuations, and negative events. This means that companies can invest more in productive endeavors, which benefits the economy.
How derivatives are used in the stock market
Derivatives are financial products that investors use to access assets they cannot trade directly. In the stock market, these products include exchange-traded funds and futures contracts. In addition, investors can hedge their stock positions with these products. But these products are complicated and require more advanced financial knowledge and active management. As a result, they may not appeal to novice and intermediate investors.
Most traders enter the derivatives market to speculate and profit. However, some enter the derivatives market to protect themselves from risk. They can use their surplus funds to purchase a hedged option. This means they can purchase an option that guarantees a certain price for six months. This way, they will avoid losing money in case the price goes down.
Derivatives are contracts that depend on the price of an underlying financial instrument. These contracts are usually made between two parties. Most derivatives are highly leveraged, so the risk-to-reward ratio is high. There are many different types of derivatives available to market participants.
What are the types of derivatives?
Derivatives are contracts between two parties that specify conditions that must be met to obtain the desired outcome. These contracts can be made on several underlying assets, such as stocks, interest rates, and currencies. Sometimes, a single asset may be derivated from several other derivatives, complicating proper valuation. One common type of derivative is a call option. The call option holder has the right to buy an underlying asset, usually at a specific price, before the maturity date. For example, a call option on crude oil can give a holder the right to purchase 100,000 barrels of crude oil at $62 per barrel before its maturity date.
Derivatives are complex financial instruments that enable investors to hedge their positions against various risks. By purchasing crude oil futures, for example, a company can reduce its risk of exposure to commodity prices. A currency forward contract is another common type of derivative. Derivatives can also help investors leverage their positions. However, these instruments are not without their downsides. The main drawbacks include counterparty risk and the inherent risks of leverage. In addition, derivatives can create a complex web of related contracts, resulting in systemic risks.
Derivatives are used in the market for two main purposes: risk management and speculation. The former is the prudent way of managing risk, while speculation involves risky opportunities to gain profit.
What is the Formula for derivatives?
The first thing that you need to understand about derivatives is that they are mathematical operations. This means that they change the value of an asset or a variable. They can be expressed in any form, including in a rate-of-change. One way to express this is by using a special notation known as the power rule. The power rule involves bringing the original exponent in front and multiplying by it. Then you can deduct one from the original exponent to find the derivative.
Another way to express a derivative is by expressing it as a partial function. This is usually done by representing the derivative as a rounded d. Often, this is written as ‘der,’ as this means “del” or “partial.” You may wonder how these derivatives can be calculated, but don’t worry; we’ve covered you.
Another way to express the derivative of a function is through the quotient rule. A derivative of a quotient equals the denominator’s derivative times the numerator’s derivative.
Conclusion
The Exchange may suspend or terminate the conclusion of derivatives contracts in certain circumstances. In these circumstances, it shall inform the Trading Participants and follow the procedures specified by regulatory legal acts of the Federal Body or the present Derivatives Rules. The resolution shall specify the duration of the suspension or termination of the conclusion of derivatives contracts.